Featured Articles
Manufacturers have two options when creating plastic parts and products: CNC plastic machining and traditional machining. The two methods possess their disadvantages as well as advantages. The understood differences can enable a business to make informed decisions about which method suits it best. What is CNC plastic machining? CNC is an abbreviation of Computer Numerical Control. In this machining, computer programs are used to operate cutting machines and tools. The machine is informed by the computer where to cut, its depth, and speed. This produces very accurate plastic components with minimal human intervention in the cutting process. The CNC plastic Machining is capable of operating on various types of plastic materials. They can cut, drill, mill, and shape plastic prototypes according to digital information. The operator inserts the plastic material into the machine and sets up the program, after which the machine performs most of the work automatically. What does Traditional Machining mean? The use of traditional machining is more manual and requires fewer skills. Machinists are talented employees who operate hand tools, conventional lathes, milling machines, and drill presses. These machines are controlled directly by them and are modified as per their experience and training. With traditional machining, the machinist should be regularly monitoring the process. They decide to slow down the speed, change tools, and the measurements during the job. This will take many years to perfect. Speed and Efficiency CNC Machining Advantages Most jobs can be performed on CNC machines, and compared to traditional methods, they are significantly faster. The program can run for hours on the machine once it is properly configured. It can operate independently, even when nobody is around or on weekends, with minimal supervision. This translates into a more efficient production of parts that require less time and effort. The CNC machine also rapidly changes between various functions. They can drill holes, cut shapes, and even smooth surfaces using one setup. This saves them the time required to transfer parts across machines. Traditional Machining Speed Traditional machining is typically more time-consuming, as every step must be performed manually. Machinist must have time to measure, modify, and examine their work at every stage. Simple jobs or single pieces can be better suited for traditional methods, as they require no programming time. Accuracy and Precision CNC Precision Benefits CNC machinery excels at producing identical parts with high precision and accuracy. The computer controls allow for everything to be exactly as designed. The latest CNC machine is capable of keeping a tolerance of thousands of an inch. Such a level of accuracy cannot be consistently achieved with manual methods. The computer also eliminates the human errors that may occur when performing repetitive work. The parts are produced in the same manner as the previous part, which is essential for mass production. Traditional Machining Accuracy Even good machinists can produce flawless precision, although they must watch it closely and be skilled. The level of skills of the particular worker also determines the level of accuracy. Although master machinists can work effectively, it becomes challenging when dealing with a large number of parts. Long lines of production may also cause human fatigue, which can compromise accuracy. Even small changes in hand pressure or tool position will accumulate over time. Cost Considerations Initial Investment The prices of CNC machines are significantly higher than those of traditional ones. One of the simplest CNC machines can cost tens of thousands of dollars, whereas traditional tools can cost considerably less. Nevertheless, a short-term cost must be offset by long-term gains. Operating Costs CNC machining can be more cost-effective per part, especially in large production runs. The machine requires minimal operator attention; therefore, lower labor costs will be incurred. Traditional machining requires an experienced operator to be involved in the entire process; therefore, larger jobs incur increased labor costs. Setup and Programming CNC machining takes time to produce and test programs before manufacturing. In small jobs, such a setup time could render CNC very costly. Traditional machining typically involves an immediate start to machining without extensive preparation. Adaptability and Flexibility. CNC Flexibility Different part designs can be easily changed, as CNC machines can be loaded with new programs. Shapes that are complex and cannot or would be challenging to create by hand can be done using CNC. This machine is also capable of forming complicated designs, correct angles, and linked curves. Nonetheless, it can be challenging to modify things during the production process. Changing the computer program could involve halting production and re-programming the machine. Traditional Machining Adaptability Traditional machining excels when modifications or changes need to be made quickly and efficiently. A skilled machinist will be able to alter his style immediately without having to pause to re-code anything. It is this that makes traditional methods best when it comes to prototype work or custom one-off work. Traditional procedures are also suitable for repair work, where the specifications may not be known in advance. The machinist can change and adjust as they proceed. Skill Requirements CNC Operation The CNC machining takes a different set of skills compared to traditional machining. The operators should be acquainted with computer programming, digital design software, and the machine setup process. The machine itself is automated to cut things; however, the operation of the machine requires technical expertise to set it up properly. CNC programming learning can be pretty steep, but once learned, operators can create more elaborate parts with less physical effort required during processing. Traditional Machining Skills Traditional machining took years of practical experience to learn. Machinists also need to learn to sense the various materials, understand the behavior of cutting tools, and know how to spot and feel quality. These competencies are gained over a long period of time, but are highly flexible. It is increasingly difficult to find skilled individuals with traditional machinist skills, as fewer people are entering the field. This may lead to increased costs in traditional machining due to higher wages paid to experienced workers. Quality and Consistency CNC Quality Control CNC machines have a very high degree of consistency. All the parts are identical to the programmed specifications. This is necessary for products that require precise fitting or those with high-quality standards. CNC quality issues typically arise from programming errors, tool wear, or machine calibration errors. As soon as these issues are resolved, the level of quality is restored to the desired extent. Traditional Quality Factors. The quality of the traditional machining is very reliant on the skill and focus of the individual machinist. Although talented employees can deliver quality outcomes, the quality may vary significantly from one operator to another, as well as within the same operator on any given day. Traditional machining is based on quality control, where inspection and measurement are performed frequently throughout the process. What is the correct Method for your Project? The selection of CNC and traditional machining is based on several factors: Choose CNC when you need: 🔹 High production volumes 🔹 The same parts with strict tolerances. 🔹 Complex shapes or patterns 🔹 Uninterrupted quality in several works. 🔹 Very little human intervention in the production process. Select the traditional machining in the cases where you possess: 🔹 Minor quantities or manufactured goods. 🔹 Basic shapes that do not demand complicated programs. 🔹 The necessity of fast changes in production. 🔹 Small capacity to fund equipment. 🔹 Experienced machinists on hand. Conclusion Both CNC machining and traditional machining hold significant functions in manufacturing today. CNC is efficient in producing high volumes of complex parts with high accuracy. Traditional machining remains important in custom machining, as well as in repair, or when flexibility is required. Both approaches are employed in many successful shops, where a particular approach is selected according to the specific job. The strengths and constraints of each method enable manufacturers to make informed decisions that improve quality at reasonable costs.
READ FULLA valve performs well when all the components inside it work properly. The production quality and durability have to be met through successful tests. Unless those successful quality tests are conducted, no valve is allowed to reach customers. Therefore, specific types of API, ASME, and ISO standards must be followed. Manufacturers conduct these tests to inspect valve seat tightness and closure for pressure maintenance. Some seat leakage testing methods help companies ensure the success of valves. These tests last from 15 seconds to 120 seconds, depending on valve size. Within this duration, quality inspectors analyze the performance and durability of valves. Hydrostatic and pneumatic tests are two main methods with slight differences you can know. These tests comply with international standards to help companies qualify for global supply. Hydrostatic Testing The first test is hydrostatic type, which includes high-pressure water. In this method, valve inspectors pass through water with higher pressure than the standard limit of the valve. Since its duration is a few seconds or minutes, they accurately inspect the signs of leakage. This method is primarily suitable for high-pressure valves where the leakage is riskier. Only water is used in this test since it is easier to clean from the valves. In this test, one end remains open, and the rest are closed. Then, the water with high pressure passes through that one end. Hydrostatic testing allows industries to detect every risk of leakage with a cheap liquid, water. Also, water is a thin liquid with low viscosity. It helps the inspectors analyze the safety level of valves better than any other liquid. Benefits of Hydrostatic Test The main benefit is that water passes through the cracks to show signs of leakage. It is suitable for normal and even tiny cracks inside the valves. Water is a thin liquid, which makes valve seat inspection more convenient. Inspectors analyze the condition of the valve by examining the number of drops per minute. This method is safer than the pneumatic method. Although water pressure is extremely high, its risk of explosion is low. It allows the inspectors to detect the leak points in the valves safely. Also, the hydrostatic test helps detect valve leakage more quickly than other methods. Water is visible on the surface of the valve, even if the cracks are not visible. Pneumatic Testing The second method is pneumatic testing, which uses gas instead of water. This method uses gas because water is not suitable for some conditions. Inspectors pass air or gas into the valve at an extremely high pressure higher than the valve's safe limit. This method is suitable when there is a risk of water contamination. Some valves have complex structures, making removing the remaining water after the test impossible. The pneumatic test helps detect leaks. It is a more sensitive test than hydrostatic testing because gas pressure is exceptionally high and hazardous. This method requires more precautions, and leaks are more challenging to detect than in the hydrostatic type. Inspectors apply soap or other chemicals to the base to detect leakage. This test uses a similar process to hydrostatic testing. Benefits of Pneumatic Test The main benefit of a pneumatic test is that it detects even minor cracks. Inspectors detect leakage by calculating the number of bubbles per minute from the crack. Pneumatic testing is suitable for non-liquid conditions where only inspectors are restricted to gas flow. Valves, where the liquid is not ideal because of corrosion risk, prove this method is the right choice. It is an ideal method for gas valves. It is the right choice for hard-to-detect leaks in sensitive applications. Back Seat Testing This type of testing is a sub-type, which is done only in a few types of valves. Only the globe and gate valves have back seats where you need to conduct this test. It works to detect stem leakage. This test plays a key role in detecting the performance of the back seat and the stem. This method keeps the valve utterly open while closing the other ends. Inspectors also remove the packing gland during this process. Then, the packing gland and stem areas are inspected for signs of leakage. Visual Inspection It is a basic inspection that detects apparent signs of leakage. Before the primary inspection, inspectors use this method to find possible cracks and signs of wear and tear, including corrosion inside the valve. Conclusion Valve inspection aims to eliminate all risks of leakage and explosion. The pressure consistency remains when there is no leakage or corrosion inside the valve. The seat stability remains as long as it is in good condition. Some liquids cause corrosion inside the valves, which leads to pressure reduction and cracks. Two primary tests are conducted pneumatic and hydrostatic tests, which help find signs of leakage.
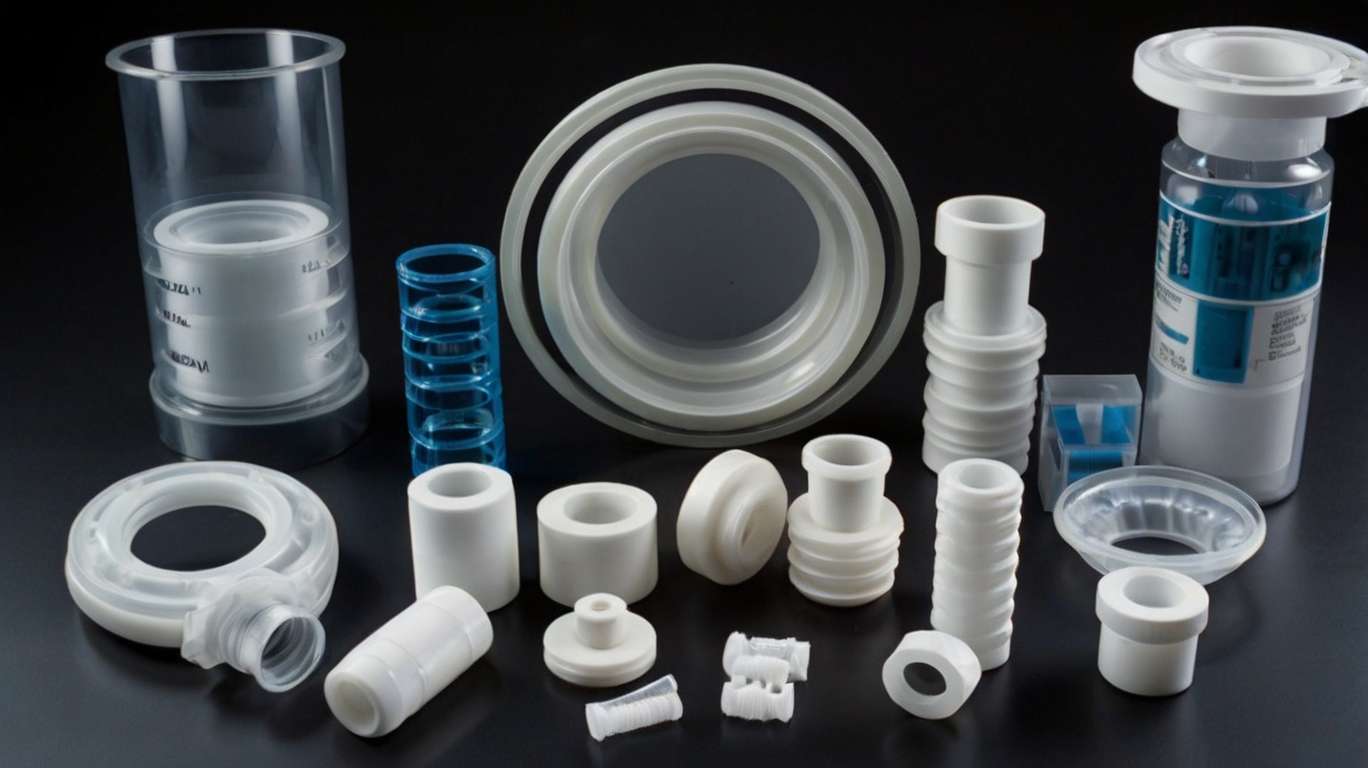
READ FULLPolytetrafluoroethylene or PTFE is a synthetic polymer that has everyone is familiar with and is utilized in a wide range of industrial sectors. Its combination of properties like thermal resistance, chemical inertness and low friction makes it highly versatile and this means that it can be used in all kinds of applications from non-stick cookware to aerospace technology. In this comprehensive guide we will explain in-depth the characteristics, applications and benefits of this fascinating polymer and what makes it so useful in the industrial sector. What is PTFE? Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) was invented by Dr. Roy Plunkett. The invention was more of a discovery by accident. Dr. Roy than trademarked the newly discovered material by the now well-known name of Teflon. Chemical Composition PTFE is a polymer which means that its chemical structure consists of only carbon and fluorine atoms chained together with a repeating formula of –(CF2-CF2)n-. The specially arranged atoms are what gives PTFE its unique qualities. Main Properties Non-stick nature: PTFE has a surface texture which is frictionless and this means that most materials cannot stick easily. Thermal Resistance: PTFE can remain stable to heat and cold across a wide temperature range from -200 Celsius to 260 Celsius so it can handle temperature fluctuations pretty well. Chemical Inertness: PTFE is corrosion resistant as it remains invulnerable to damage by most chemicals including acids, alkalis and solvents. Low Friction Coefficient: PTFE has a smooth surface that generates almost no friction and its coefficient is the lowest among solids. High Electrical Insulation: PTFE is not a conductor of electricity so it is widely used to insulate the electrical applications. How is PTFE made? The manufacturing procedure of PTFE involves the polymerization of tetrafluoroethylene (TFE), which is a reactive and flammable gas. The polymerization is done under specific conditions utilizing an initiator. The result is a stable polymeric structure. After the stage of polymerization PTFE is processed into different shapes like flat sheet, rod or coating. The shapes are made through extrusion, molding, and sintering processes for custom applications. Applications of PTFE PTFE is a material that is used extensively in many sectors because it has a large variety of properties. Let us look at PTFE applications in detail. Non-stick Cookware One of the most popular applications of PTFE is non-stick frying pans and cookware. A layer of PTFE is applied to prevent the food from sticking on the surface. This makes pots and pans easy to clean. Industrial Applications Gaskets and seals are made from PTFE polymer as it is resistant to chemicals. The seals are used to cover chemical pipelines and water pipes. Bearings and bushings is another useful item made from PTFE. The low friction coefficient is vital for smooth movement in moving parts. Filters: Filtration systems are fitted with PTFE membranes as this polymer has a robust build and is corrosion resistant. Electrical Applications PTFE is a common material used for insulation of cable wires. In high voltage areas this polymer provides foolproof protection. The dielectric qualities of this plastic also reduce energy dissipation. Medical Industry Implants and prosthetics are made from PTFE, as this material does not cause any allergy. Surgical Tools are manufactures using this material as the non-adhesive nature means that the tissue does not stick to the tool which enhances surgical efficiency. Catheters and tubing is another medical tool that is made from the polymer as it has a smooth surface and is chemically inert. Aerospace and Automotive Industries In aerospace PTFE is utilized for construction of seals and gaskets as it can tolerate temperature fluctuations and chemically corrosive exposure. Automotive industries make use of PTFE for coating engine components, and transmission systems. Textile Industry In textiles a layer of PTFE can make cloth water-resistant and stain-proof which is crucial for sportswear. Future Trends of PTFE Versatility: PTFE can be used in various industries because of its distinct properties. Durability: It has a robust build and can tolerate exposure to harsh conditions like extreme temperatures, corrosive chemicals, and heavy use. Low Maintenance: Due to its non-stick and inert nature, it is easy to clean up and its use minimizes maintenance. Safety and Biocompatibility: It is safe for use in medical applications and food-grade products. Environmentally Resistant: It is stable under UV exposure, moisture, and weathering, ensuring its long service life. Modified PTFE: Expanded PTFE is engineered to show increased flexibility and porosity, and thus this material has several applications in advanced filtration systems, medical implants. Sustainability: Developing greener chemistry for PTFE to help reduce environmental burden Integration with Nanotechnology: When nanoparticles are included in the compound, mechanical and thermal strengths improve. 3D Printing with PTFE: Emerging techniques are making it possible to use PTFE in additive manufacturing, thereby opening new avenues for customized applications. Compared to other synthetic polymers, PTFE has some exclusive properties: PTFE vs. Nylon: While nylon has greater mechanical strength, PTFE has superior chemical resistance and non-stick properties. PTFE vs. Polyethylene: Polyethylene is cheaper but not comparable to PTFE's thermal stability and low friction coefficient. PTFE vs. Silicone: Silicone is more flexible and better suited for certain applications like medical tubing, but it lacks the non-stick nature and chemical inertness of PTFE. Conclusion PTFE is a revolutionary material that has raised performance standards for a wide variety of industries. Its excellent properties-these are its heat resistance, chemical inertness, and non-stick property-make it an indispensable component in applications as varied as non-stick cookware and advanced aerospace systems. Despite all the shortcomings, PTFE is a pillar of modern material science and will continue to adapt to the challenges of new demands in technology. With innovation pushing forward modified and sustainable variants, the role of PTFE in the future of manufacturing and engineering will grow.
READ FULL